
Research Direction:
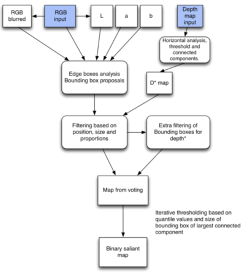
AI in Computer Vision: 2D/3D scene understanding, saliency, object detection and recognition A multi-stage approach is proposed for salient object detection in natural images which incorporates color and depth information. In the first stage, color and depth channels are
incorporates color and depth information. In the first stage, color and depth channels are explored separately through objectness-based measures to detect potential regions containing
salient objects. This procedure produces a list of bounding boxes which are further filtered and
refined using statistical distributions. The retained candidates from both color and depth
explored separately through objectness-based measures to detect potential regions containing
salient objects. This procedure produces a list of bounding boxes which are further filtered and
refined using statistical distributions. The retained candidates from both color and depth channels are then combined using a voting system. The final stage consists of combining the
channels are then combined using a voting system. The final stage consists of combining the extracted candidates from color and depth channels using a voting system that produces a final
map narrowing the location of the salient object.
Publications:
extracted candidates from color and depth channels using a voting system that produces a final
map narrowing the location of the salient object.
Publications:  •
F. Audet, M.S. Allili, and A.-M. Cretu, "Salient Object Localisation in Images by
•
F. Audet, M.S. Allili, and A.-M. Cretu, "Salient Object Localisation in Images by Combining Objectness Clues in the RGB-D Space", Karray F., Campilho A., Cheriet F.
Combining Objectness Clues in the RGB-D Space", Karray F., Campilho A., Cheriet F. (eds) Image Analysis and Recognition. ICIAR 2017, pp. 247-255, Lecture Notes in
(eds) Image Analysis and Recognition. ICIAR 2017, pp. 247-255, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 10317. Springer.
Computer Science, vol. 10317. Springer.
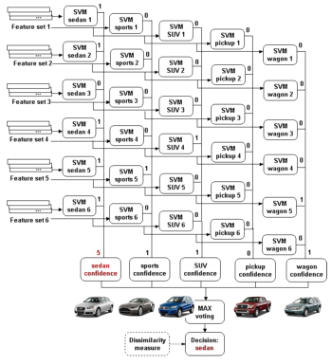
This project investigates novel approaches for building identification in aerial images, that
combine classical segmentation algorithms, user guided training approaches and supervised
learning solutions.
Support: Publications: • J. Tremblay-Gosselin and A.-M. Cretu, "A Supervised Training and Learning Method for Building Identification in Remotely Sensed Images", IEEE Int. Symp. Robotic and Sensors Environments, Washington, US, 21-23 Oct. 2013, pp.73-78. • A.-M. Cretu, and P. Payeur, "Building Detection in Aerial Images Based on Watershed and Visual Attention Feature Descriptors", Canadian Conf. Computer and Robot Vision, pp. 265-272, Regina, 2013. • A.-M. Cretu, "Evolving Sensor System Environments with Visual Attention: An Experimental Exploration", Proc. IEEE Symp. Robotic and Sensors Environments, pp. 97-102, Magdeburg, Germany, 16-18 Nov. 2012 (invited talk). Drawing inspiration from the significantly superior performance of humans to extract and interpret visual information, the proposed research transposes the visual attention
interpret visual information, the proposed research transposes the visual attention mechanisms into biologically-inspired computational systems to develop new techniques and
computational resources capable to interpret complex images with large variations in their
mechanisms into biologically-inspired computational systems to develop new techniques and
computational resources capable to interpret complex images with large variations in their content and characteristics. The project is dedicated to the exploration, implementation,
content and characteristics. The project is dedicated to the exploration, implementation, refinement and validation of a series of biologically-inspired computational models for
refinement and validation of a series of biologically-inspired computational models for attention and object recognition dedicated to specific tasks, such as building detection in the
context of geo-imaging.
Collaborators/ Support:
attention and object recognition dedicated to specific tasks, such as building detection in the
context of geo-imaging.
Collaborators/ Support: Publications:
Publications: •
A.-M. Cretu, and P. Payeur, "Visual Attention Model with Context Learning for Building
Detection in Satellite Images", Int. Journal Smart Sensing and Intelligent Systems, vol. 5, no.4, pp. 742-766, Dec. 2012.
•
M. I. Sina, P. Payeur, and A.-M. Cretu, "Object Recognition on Satellite Images with Biologically-Inspired Computational Approaches",
IEEE Int. Symp. Applied Computational Intelligence and Informatics, pp. 81-86, Timisoara, Romania, 24-26 May 2012.
•
M. I. Sina, A.-M. Cretu, and P. Payeur, “Biological Visual Attention Guided Automatic Image Segmentation with Application in Satellite
Imaging”, Proc. IS&T/SPIE Electronic Imaging Conference, Human Vision and Electronic Imaging Track, vol. 8291, Burlingame,
California, USA, Jan. 2012.
The automated servicing of vehicles is becoming more and
more a reality in today’s world. While certain operations,
•
A.-M. Cretu, and P. Payeur, "Visual Attention Model with Context Learning for Building
Detection in Satellite Images", Int. Journal Smart Sensing and Intelligent Systems, vol. 5, no.4, pp. 742-766, Dec. 2012.
•
M. I. Sina, P. Payeur, and A.-M. Cretu, "Object Recognition on Satellite Images with Biologically-Inspired Computational Approaches",
IEEE Int. Symp. Applied Computational Intelligence and Informatics, pp. 81-86, Timisoara, Romania, 24-26 May 2012.
•
M. I. Sina, A.-M. Cretu, and P. Payeur, “Biological Visual Attention Guided Automatic Image Segmentation with Application in Satellite
Imaging”, Proc. IS&T/SPIE Electronic Imaging Conference, Human Vision and Electronic Imaging Track, vol. 8291, Burlingame,
California, USA, Jan. 2012.
The automated servicing of vehicles is becoming more and
more a reality in today’s world. While certain operations, such as car washing, require only a rough model of the
such as car washing, require only a rough model of the surface of a vehicle, other operations, such as changing of
surface of a vehicle, other operations, such as changing of a wheel or filling the gas tank, require correct localization of
the different parts of the vehicle on which operations are to
a wheel or filling the gas tank, require correct localization of
the different parts of the vehicle on which operations are to be performed. The proposed image-based approach to
be performed. The proposed image-based approach to roughly localize vehicle parts over the surface of a vehicle
roughly localize vehicle parts over the surface of a vehicle with a bounding box approach is based on a model of
with a bounding box approach is based on a model of human visual attention. The proposed method is
human visual attention. The proposed method is automatically adapted for different views of a vehicle and
automatically adapted for different views of a vehicle and obtains average localization rates for different vehicle parts
obtains average localization rates for different vehicle parts of over 95% for a dataset of 120 vehicles belonging to three categories, namely sedan, SUV and wagon and allows, with the addition of the
of over 95% for a dataset of 120 vehicles belonging to three categories, namely sedan, SUV and wagon and allows, with the addition of the active contour models, for a more complete and accurate description of vehicle parts contours than other state-of-the-art solutions.
Collaborators/ Support:
active contour models, for a more complete and accurate description of vehicle parts contours than other state-of-the-art solutions.
Collaborators/ Support: Publications:
Publications: •
D. Nakhaeinia, P. Payeur, A. Chávez-Aragón, A.-M. Cretu, R. Laganière, and R. Macknojia, “Surface Following with an RGB-D Vision-
Guided Robotic System for Vehicle Security Screening”, Int. Journal Smart Sensing and Intelligent Systems, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 419-447,
Jun. 2016.
•
A.-M. Cretu, P. Payeur, R. Laganière, "An Application of a Bio-Inspired Visual Attention Model Guided for the Localization of Vehicle
Parts", Applied Soft Computing, vol.31. pp. 369-380, 2015.
•
R. Fareh, P. Payeur, D. Nakhaeinia, R. Macknojia, A. Chávez-Aragón, A.-M. Cretu, P. Laferrière, R. Laganière. R. Toledo, "An
Integrated Vision-Guided Robotic System for Rapid Vehicle Inspection", IEEE Int. Systems Conference, SysCon, Ottawa, Mar. 2014
(Best Paper Award).
•
A.-M. Cretu, P. Payeur, "Image-Based Localization of Vehicle Parts Guided by Visual Attention", Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Instrumentation
and Measurement Technology, pp. 533-538, Graz, Austria, May 2012.
The continuous rise in the amount of vehicles in circulation brings an increasing
need for automatically and efficiently recognizing vehicle categories for multiple
applications such as optimizing available parking spaces, balancing ferry
•
D. Nakhaeinia, P. Payeur, A. Chávez-Aragón, A.-M. Cretu, R. Laganière, and R. Macknojia, “Surface Following with an RGB-D Vision-
Guided Robotic System for Vehicle Security Screening”, Int. Journal Smart Sensing and Intelligent Systems, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 419-447,
Jun. 2016.
•
A.-M. Cretu, P. Payeur, R. Laganière, "An Application of a Bio-Inspired Visual Attention Model Guided for the Localization of Vehicle
Parts", Applied Soft Computing, vol.31. pp. 369-380, 2015.
•
R. Fareh, P. Payeur, D. Nakhaeinia, R. Macknojia, A. Chávez-Aragón, A.-M. Cretu, P. Laferrière, R. Laganière. R. Toledo, "An
Integrated Vision-Guided Robotic System for Rapid Vehicle Inspection", IEEE Int. Systems Conference, SysCon, Ottawa, Mar. 2014
(Best Paper Award).
•
A.-M. Cretu, P. Payeur, "Image-Based Localization of Vehicle Parts Guided by Visual Attention", Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Instrumentation
and Measurement Technology, pp. 533-538, Graz, Austria, May 2012.
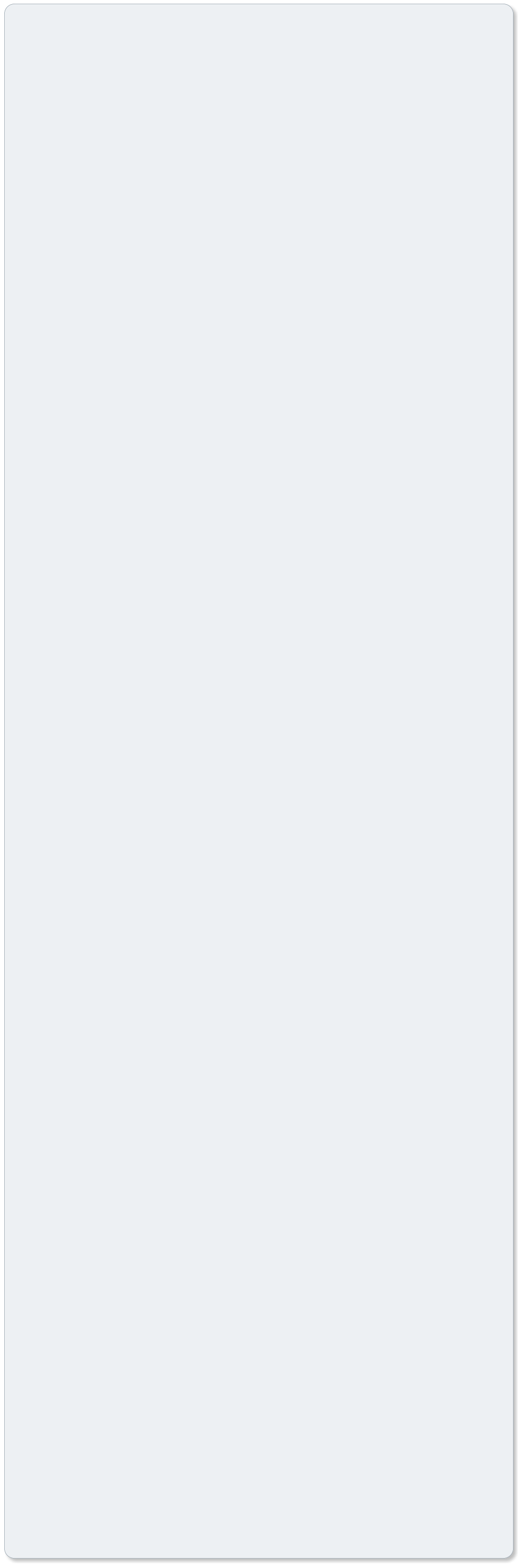
The continuous rise in the amount of vehicles in circulation brings an increasing
need for automatically and efficiently recognizing vehicle categories for multiple
applications such as optimizing available parking spaces, balancing ferry space, perceiving highway toll, planning infrastructure and managing traffic, or
servicing vehicles. This project describes the design and implementation of a
vehicle classification system using a set of images collected from 6 views. The
proposed computational system combines human visual attention mechanisms
to identify a set of salient discriminative features and a series of binary support
vector machines to achieve fast automated classification.
Collaborators/ Support:
space, perceiving highway toll, planning infrastructure and managing traffic, or
servicing vehicles. This project describes the design and implementation of a
vehicle classification system using a set of images collected from 6 views. The
proposed computational system combines human visual attention mechanisms
to identify a set of salient discriminative features and a series of binary support
vector machines to achieve fast automated classification.
Collaborators/ Support: Publications:
Publications: •
A.-M. Cretu, and P. Payeur, "Biologically-Inspired Visual Attention
Features for a Vehicle Classification Task", Int. Journal Smart Sensing
and Intelligent Systems, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 402-423, Sep. 2011.
•
A.-M. Cretu, P. Payeur, and R. Laganière, "Salient Features Based on
Visual Attention for Multi-View Vehicle Classification", Proc. IEEE Int.
Conf. Computational Intelligence for Measurement Systems and
Applications, pp. 64-69, Ottawa, Canada, Sep. 2011.
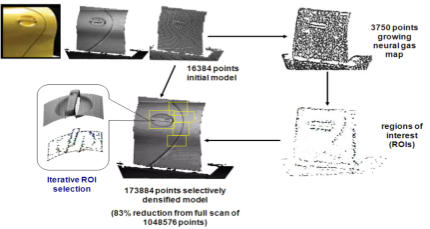
This project explores some aspects of intelligent sensing for
•
A.-M. Cretu, and P. Payeur, "Biologically-Inspired Visual Attention
Features for a Vehicle Classification Task", Int. Journal Smart Sensing
and Intelligent Systems, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 402-423, Sep. 2011.
•
A.-M. Cretu, P. Payeur, and R. Laganière, "Salient Features Based on
Visual Attention for Multi-View Vehicle Classification", Proc. IEEE Int.
Conf. Computational Intelligence for Measurement Systems and
Applications, pp. 64-69, Ottawa, Canada, Sep. 2011.
This project explores some aspects of intelligent sensing for advanced robotic applications, with the main objective of
advanced robotic applications, with the main objective of designing innovative approaches for automatic selection of
designing innovative approaches for automatic selection of regions of observation for fixed and mobile sensors to collect
regions of observation for fixed and mobile sensors to collect only relevant measurements without human guidance. The
only relevant measurements without human guidance. The proposed neural gas network solution selects regions of
proposed neural gas network solution selects regions of interest for further sampling from a cloud of sparsely collected
3D measurements. The technique automatically determines
interest for further sampling from a cloud of sparsely collected
3D measurements. The technique automatically determines bounded areas where sensing is required at higher resolution
to accurately map 3D surfaces. Therefore it provides significant
benefits over brute force strategies as scanning time is reduced
and the size of the dataset is kept manageable.
Collaborators/ Support:
bounded areas where sensing is required at higher resolution
to accurately map 3D surfaces. Therefore it provides significant
benefits over brute force strategies as scanning time is reduced
and the size of the dataset is kept manageable.
Collaborators/ Support:  Publications:
Publications: •
P. Payeur, P. Curtis, A.-M. Cretu, "Computational Methods for Selective Acquisition of Depth Measurements: an Experimental
Evaluation", Int. Conf.
Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems, Poznan, Poland, J. Blanc-Talon et al. (Eds.) LNCS 8192, pp. 389-401, 2013.
•
P. Payeur, P. Curtis, A.-M. Cretu, "Computational Methods for Selective Acquisition of Depth Measurements in Machine Perception",
IEEE Int. Conf. Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Manchester, UK, pp.876-881, 2013.
•
A.-M. Cretu, P. Payeur, and E.M. Petriu, “Selective Range Data Acquisition Driven by Neural Gas Networks”, IEEE Trans.
Instrumentation and Measurement, vol. 58, no. 6, pp. 2634-2642, 2009.
•
A.-M. Cretu, P. Payeur, and E.M. Petriu, “Neural Gas and Growing Neural Gas Networks for Selective 3D Sensing: A Comparative
Study”, Sensors & Transducers, vol. 5, pp. 119-134, 2009.
•
A.-M. Cretu, P. Payeur, and E.M. Petriu, “Selective Tactile Data Acquisition on 3D Deformable Objects for Virtualized Reality
Applications”, Proc. IEEE Int. Workshop Computational Intelligence in Virtual Environments, pp.14-19, Nashville, TN, USA, Apr. 2009
•
A.-M. Cretu, E.M. Petriu, and P. Payeur, “Growing Neural Gas Networks for Selective 3D Scanning”, Proc. IEEE Int. Workshop on
Robotic and Sensors Environments, pp. 108-113, Ottawa, Canada, Oct. 2008.
•
A.-M. Cretu, P. Payeur, and E.M. Petriu, “Selective Vision Sensing Based on Neural Gas Network”, Proc. IEEE Int. Conf.
Instrumentation and Measurement Technology, pp. 478-483, Vancouver, Canada, May 2008 (Best Student Paper Award).
•
P. Payeur, P. Curtis, A.-M. Cretu, "Computational Methods for Selective Acquisition of Depth Measurements: an Experimental
Evaluation", Int. Conf.
Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems, Poznan, Poland, J. Blanc-Talon et al. (Eds.) LNCS 8192, pp. 389-401, 2013.
•
P. Payeur, P. Curtis, A.-M. Cretu, "Computational Methods for Selective Acquisition of Depth Measurements in Machine Perception",
IEEE Int. Conf. Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Manchester, UK, pp.876-881, 2013.
•
A.-M. Cretu, P. Payeur, and E.M. Petriu, “Selective Range Data Acquisition Driven by Neural Gas Networks”, IEEE Trans.
Instrumentation and Measurement, vol. 58, no. 6, pp. 2634-2642, 2009.
•
A.-M. Cretu, P. Payeur, and E.M. Petriu, “Neural Gas and Growing Neural Gas Networks for Selective 3D Sensing: A Comparative
Study”, Sensors & Transducers, vol. 5, pp. 119-134, 2009.
•
A.-M. Cretu, P. Payeur, and E.M. Petriu, “Selective Tactile Data Acquisition on 3D Deformable Objects for Virtualized Reality
Applications”, Proc. IEEE Int. Workshop Computational Intelligence in Virtual Environments, pp.14-19, Nashville, TN, USA, Apr. 2009
•
A.-M. Cretu, E.M. Petriu, and P. Payeur, “Growing Neural Gas Networks for Selective 3D Scanning”, Proc. IEEE Int. Workshop on
Robotic and Sensors Environments, pp. 108-113, Ottawa, Canada, Oct. 2008.
•
A.-M. Cretu, P. Payeur, and E.M. Petriu, “Selective Vision Sensing Based on Neural Gas Network”, Proc. IEEE Int. Conf.
Instrumentation and Measurement Technology, pp. 478-483, Vancouver, Canada, May 2008 (Best Student Paper Award).

Research
© Ana-Maria Cretu 2019
Ana-Maria Cretu



Neuro-inspired computational intelligence for geo-imaging systems






Localization of vehicle parts guided by visual attention

Salient features for image-based vehicle classification

Computational intelligence for pattern recognition in aerial imaging


Salient object detection in RGB-D data

Selective range data acquisition